Are you new to academia? Do you want to learn how to write a good review paper to get in-depth knowledge about your domain? you are at the right place. In this article, you will learn how to write the best review paper in a step-by-step systematic procedure with a sample review article format to get more citations during you doctoral degree.
What is a Review Paper?
A review paper, or a literature review, is a thorough, analytical examination of previously published literature. It also chronologically overviews current research works on a particular topic.
- The main objective of writing a review paper is to evaluate the existing data or results, which can be done through analysis, modeling, classification, comparison, and summary.
- Review papers can help to identify the research gaps, to explore potential areas in a particular field.
- It helps to come out with new conclusions from already published works.
- Any scholar or researcher or scientist who wants to carry out research on a specific theme, first read the review articles relevant to that research area to understand the research gap for arriving at the problem statement.
- Writing a review article provides clarity, novelty, and contribution to the area of research and it demands a great level of in-depth understanding of the subject and a well-structured arrangement of discussions and arguments.
- Some journals publish only review papers, and they do not accept research articles. It is important to check the journal submission guidelines.
Difference Between a Review Paper and a Research Paper
The review paper differs from a research paper in three main ideas that is: perspectives, content, and length, as follows.
| Review paper | Research paper | |
| Perspective | Evaluates previously published literatures on a specific topic | Discusses the present research findings of an author |
| Content | Existing research data | New experimental findings |
| Length | Longer than a research article. | Discusses the present research findings of the author |
Also, it can be further differentiated in the 50 important points in the next section.
Research Paper Vs Review Paper | 50 Differences

- A research paper is typically much longer than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more detailed and comprehensive than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more focused on a specific topic than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more analytical and critical than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more objective than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically written by one or more authors, while a review paper may be written by a single author.
- A research paper is typically peer-reviewed, while a review paper may not be.
- A research paper is typically published in a scholarly journal, while a review paper may be published in a variety of different publications.
- The audience for a research paper is typically other scholars, while the audience for a review paper may be the general public.
- The purpose of a research paper is typically to contribute to the scholarly literature, while the purpose of a review paper may be to provide an overview of the literature or to evaluate a particular research study.
- The structure of a research paper is typically more complex than the structure of a review paper.
- A research paper typically includes an abstract, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a literature review, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a methodology section, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes results and discussion sections, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a conclusion, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper is typically organized around a central research question, while a review paper may be organized around a central theme.
- A research paper typically uses primary sources, while a review paper may use both primary and secondary sources.
- A research paper is typically based on empirical research, while a review paper may be based on either empirical or non-empirical research.
- A research paper is typically more formal than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically written in the third person, while a review paper may be written in the first person.
- A research paper typically uses formal language, while a review paper may use more informal language.
- A research paper is typically objective in tone, while a review paper may be more subjective in tone.
- A research paper typically uses APA style, while a review paper may use a different style.
- A research paper typically includes a title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes an abstract on the title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes keywords on the title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes an author note, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a literature review, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a methodology section, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes results and discussion sections, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes a conclusion, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper is typically organized around a central research question, while a review paper may be organized around a central theme.
- A research paper typically uses primary sources, while a review paper may use both primary and secondary sources.
- A research paper is typically based on empirical research, while a review paper may be based on either empirical or non-empirical research.
- A research paper is typically longer than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more detailed and comprehensive than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more focused on a specific topic than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more analytical and critical than a review paper.
- A research paper is typically more objective than a review paper.
- The audience for a research paper is typically other scholars, while the audience for a review paper may be the general public.
- The purpose of a research paper is typically to contribute to the scholarly literature, while the purpose of a review paper may be to provide an overview of the literature or to evaluate a particular research study.
- The structure of a research paper is typically more complex than the structure of a review paper.
- A research paper typically uses APA style, while a review paper may use a different style.
- A research paper typically includes a title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes an abstract on the title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes keywords on the title page, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper typically includes an author note, while a review paper may not.
- A research paper is typically written in the third person, while a review paper may be written in the first person.
- A research paper typically uses formal language, while a review paper may use more informal language.
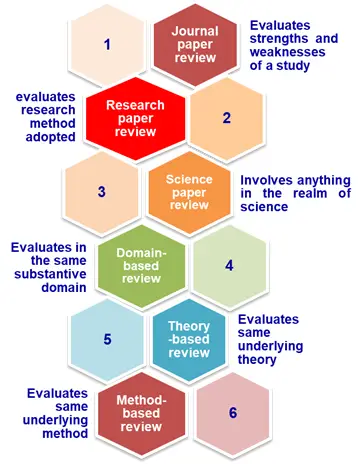
6 Types of Review Papers
The review papers are classified in to six main categories based on the theme and it is presented in the figure below.
Purpose of Review Paper
The purpose of a review paper is to assess a particular research question, theoretical or practical approach which provides readers with in-depth knowledge and state-of-the-art understanding of the research area.
The purpose of the review paper can vary based on their specific type and research needs.
- Provide a unified, collective overview of the current state of knowledge on a specific research topic and provide an inclusive foundation on a research theme.
- Identify ambiguity, and contradictions in existing results or data.
- Highlight the existing methodological approaches, research techniques, and unique perceptions.
- Develop theoretical outlines to resolve and work on published research.
- Discuss research gaps and future perspectives.
Criteria for a Good Review Paper
A good review paper needs to achieve three important criteria. (Palmatier et al 2017).
- First, the area of research should be suitable for writing a review paper so that the author finds sufficient published literature.
- The review paper should be written with suitable literature, detailed discussion, sufficient data/results to support the interpretation, and a persuasive language style.
- A completed review paper should provide substantial, new innovative ideas to the readers based on the comparison of published works.
Review papers are widely read by many researchers and it helps to get more citations for the author. So, it is important to learn how to write a review paper and find a journal to publish.
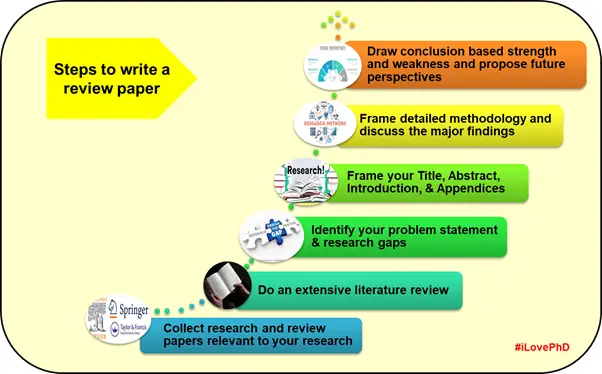
Step-by-Step Systematic Procedure to Write a Review Paper
Time needed: 20 days and 7 hours
The systematic procedural steps to write the best review paper are as follows:
- Topic selection
Select a suitable area in your research field, formulate clear objectives, and prepare the specific research hypotheses that are to be explored.
- Research design
Designing your research work is an important step for any researcher. Based on the objectives, develop a clear methodology or protocol to review a review paper.
- Data collection
Thorough analysis and understanding of different published works help the author to identify suitable and relevant data/results that will be used to write the paper.
- Data analysis
The degree of analysis to evaluate the collected data varies by extensive the review. The examination of trends, patterns, ideas, comparisons, and relationships in the study provides deeper knowledge on that area of research.
- Report
The interpretation of results is very important for a good review paper. The author should present the discussion systematically without any ambiguity.
The results can be presented in descriptive form, tables, and figures. The new insights should have an in-depth discussion of the topic in line with fundamentals. Finally, the author is expected to present the limitations of the existing study with future perspectives.
Sample Review Article Format
Title, Abstract, Keywords
Write an effective and suitable title, abstract, and keywords relevant to your review paper. This will maximize the visibility of your paper online for the readers to find your work. Your title and abstract should be clear, concise, appropriate, and informative.
Introduction
Present a detailed introduction to your research, which is published in chronological order in your own words. Don’t summarize the published literature. The introduction should encourage the readers to read your paper.
Various topics to discuss the critical issues
Make sure you present a critical discussion, not a descriptive summary of the topic. If there is contradictory research in your area of research, verify to include an element of debate and present both sides of the argument. A good review paper can resolve the conflict between contradictory works.
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
The written review paper should achieve your objectives. Hence, the review paper should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the following questions:
What they can understand from the review paper?
What still remains a requirement of further investigation in the research area?
This can include making suggestions for future scope on the theme as part of your conclusion.
Acknowledgment
The authors can submit a brief acknowledgment of any financial, instrumentation, and academic support received about research work.
References
Citing references at appropriate places in the article is necessary and important to avoid plagiarism. Each journal has its own referencing style. Therefore, the references need to be listed at the end of the manuscript. The number of references in the review paper is usually higher than in a research paper.
I hope this article will give you a clear idea of how to write a review paper. Please give your valuable comments.
iLovePhD
Learn to Research
Find Journals to Publish

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ): How to Write a Review Paper
1. What is the format of a review paper?
A review paper usually follows this format:
Title, Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Main Body (thematic or chronological), Conclusion, and References. Use subheadings to organize major sections and include citations to support your analysis.
2. How to write a review example?
Start with a clear introduction, highlight key findings from multiple studies, organize them under themes, critically compare them, and end with a conclusion that identifies research gaps. Use proper citations throughout.
3. What is the outline of a review paper?
A typical outline includes:
- Title
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Review of Literature
- Critical Analysis
- Summary & Future Directions
- References
4. How to structure a review?
Organize it either chronologically (based on the time of publication) or thematically (grouped by topic or trend). Maintain a logical flow and use headings to guide the reader.
5. What is the sequence of a review paper?
The sequence is: Title → Abstract → Introduction → Body → Summary → Conclusion → References. Each part must link well to maintain flow and clarity.
6. How long should a review paper be?
It can range from 3000 to 7000 words, depending on the journal or academic level. Always follow specific guidelines given by your institution or target publication.
7. Can anyone write a review paper?
Yes, but you need a deep understanding of the topic, good analytical skills, and proper citation knowledge. It’s essential to critically evaluate and synthesize the literature.
8. How do you plan a review paper?
Select a topic, gather research articles, organize them, write summaries, critically compare them, and structure the review with headings. Always keep your target audience in mind.
9. How do you write a review paper step by step?
- Choose a focused topic
- Collect credible sources
- Read and take notes
- Organize your points
- Write the introduction, body, and conclusion
- Add references
- Proofread and format it properly
10. What is considered a review paper?
A review paper is a scholarly article that summarizes, evaluates, and synthesizes existing research on a specific topic. It does not present new experimental data.
11. What is the structure of a review article?
- Introduction (define the topic)
- Methods (if it’s a systematic review)
- Body (analysis, comparison)
- Conclusion (key findings, research gaps)
- References
12. What is the difference between a review paper and a research paper?
A research paper presents new experimental findings.
A review paper analyzes existing research to offer insights, trends, and gaps.
13. How do you start writing a review paper?
Begin with a compelling introduction, define your topic, mention its importance, and explain how your review is structured.
14. Is writing a review paper hard?
It can be challenging at first, but becomes easier with practice. It requires strong reading, summarizing, and critical thinking skills.
15. What is review writing examples?
Example:
“Smith et al. (2021) found that AI improves diagnosis accuracy. However, Brown (2022) noted ethical issues. This contrast shows the gap in regulatory frameworks.”
16. What is the 5 C’s of writing a literature review?
- Compare studies
- Contrast findings
- Critique methodologies
- Connect the dots
- Conclude with key insights
17. What are the 5 rules for writing a literature review?
- Stay focused on the research question
- Use credible sources
- Organize logically
- Cite correctly
- Summarize and synthesize findings, not just describe them
18. What are the 3 parts of literature review?
- Introduction – Sets the scope
- Main body – Discusses studies grouped by theme/trend
- Conclusion – Highlights gaps and future research
19. What should a good literature review include?
It should include relevant studies, critical comparison, synthesis of findings, identification of research gaps, and proper citations.
20. How to avoid pitfalls when doing a literature review?
Avoid:
- Plagiarism
- Listing studies without synthesis
- Using outdated or non-peer-reviewed sources
- Overloading the reader with too much data
21. What is the 5 paragraph structure?
It includes:
- Intro
- Background info
- Body Paragraph 1
- Body Paragraph 2
- Conclusion
This structure is common in essay-style reviews.
22. Can a literature review be 5 pages?
Yes, if you’re doing a brief review or academic assignment. However, journal-level reviews are usually longer.
23. Can a literature review be 500 words?
Yes, but it will be very brief and is suitable only as a section in a larger paper, not a standalone review.
24. How many words should be in a literature review?
For standalone papers: 3000–7000 words. For thesis chapters: 1500–4000 words. Always check your institution’s guidelines.
25. How do I increase my paper citations?
You can increase citations by sharing your work widely, publishing in open-access journals, using impactful keywords, and collaborating with well-known researchers.
26. What makes a paper highly cited?
A highly cited paper typically addresses a novel, relevant, and impactful topic, uses rigorous methods, and has clear, concise writing.
27. How do you add citations easily?
Use reference management tools like Zotero, Mendeley, or EndNote to add citations efficiently and format them accurately.
28. Is 20 citations for a paper good?
Yes, having 20 citations can be considered good, but it depends on the field and the time since publication.
29. What is citation boosting?
Citation boosting involves strategies like promoting your paper online, networking with other researchers, and ensuring visibility in academic platforms.
30. How do you add citations to a research paper?
Insert citations using inline referencing formats like APA, MLA, or Chicago, depending on the journal’s requirements.
31. What influences the number of citations?
Factors like the topic’s relevance, publication journal, readability, and accessibility impact the number of citations.
32. How do I increase citation flow?
Enhance citation flow by using proper keywords, publishing in open access, and networking at conferences.
33. How do I increase the h-index in Google Scholar?
To increase your h-index, publish high-quality papers, collaborate with peers, and promote your work through academic networks.
34. Do review papers get more citations?
Yes, review papers tend to get more citations as they summarize existing research, making them valuable to other researchers.
35. How many papers get 1000 citations?
Only a small percentage of papers reach 1000 citations, usually in high-impact journals or groundbreaking fields.
36. What percentage of papers are never cited?
Research shows that about 20-30% of papers are never cited, often due to limited visibility or relevance.
37. How do I find the most cited paper?
Search databases like Google Scholar, Scopus, or Web of Science and sort by the number of citations.
38. How many references should a review paper have?
The number of references depends on the scope of the review, but typically 50-200 references are common.
39. How do you give citations in a research paper?
Citations are given in the format prescribed by the journal, such as APA, MLA, or Vancouver.
40. Can I cite under review papers?
No, you should avoid citing under-review papers as they are not yet published or verified.
41. How do I add a citation in a literature review?
In a literature review, summarize the study and cite it in-text and in the bibliography.
42. What is the best citation style for papers?
The best citation style depends on the journal or field; APA, MLA, and Chicago are popular choices.
43. How do citations increase credibility?
Citations show that your work is well-researched and backed by existing literature, adding credibility.
44. Why is it essential to properly cite sources in a literature review?
Proper citations ensure that you give credit to original authors and avoid plagiarism.
45. How do I cite references in a review paper?
Use inline citations in the text and list all references at the end in the required format.
46. What is the role of keywords in citations?
Keywords improve the discoverability of your paper, leading to more citations.
47. How do I make citations easier?
Use citation management tools to organize and format references automatically.
48. How do I write a highly cited paper?
Focus on a novel, impactful topic, ensure rigorous research, and write in clear, concise language.
49. How do citations improve your research report?
They show the depth of your research and connect your findings to the existing literature.
50. Bonus: How to End a Review Paper?
Summarize the key findings, highlight gaps, and suggest future research directions. Keep it concise and impactful.
Thank You!



Nice thank you for your clarification
How to write a review paper on the relevant of science to education
This blog is very informative. Is it true that an increase in the number of citations improves the quality and impact of a review paper?
Thanks for your ideas. Really helpful
it was very well information
As the best PhD Guidance, we just want to make this PhD journey somewhat smoother. HIGS offers the best PhD help & support for clients across the globe from various subject lines. We will help you with part-time and full-time PhD. At every stage of the research work, we make sure that your work has been completed within a given timeframe and at the lowest possible rate. Our team will help you from the stage of PhD admission to the guideship process. We help you in admission, proposal writing, review paper writing, thesis writing, editing, journal publication, implementation, viva process, guideship, and more. “HIGS- the best PhD guidance & services always stands with you in achieving your research goal through your most prestigious PhD degree”