What is Blockchain?
“Everything will be tokenized and connected by a blockchain one day”–Fred Ehrsam (American Businessman)
-
- The blockchain is a list of blocks or transaction records which are linked with each other, also secured with high-level cryptographic algorithms.
- A block is a record of new transactions – It can be a cryptocurrency, voting record, or even medical data.
- Each and every block record consist of transaction information, time of the transaction, and previous record’s link.
- Blockchains are difficult to crack and impossible to modify the transaction information.
How it differs from normal central banking system?
Blockchain peer to peer system |
Central banking system |
| The blockchain is managed by a peer-to-peer network that observes and validate the new blocks in the chain. | All transactions are only validated by authorized banking management. |
| Other people may not know your identity, but they know exactly how much value has been transferred from one person to another. | Since everything is managed by the central system, others could identify neither identity nor how much amount transferred. |
| A distributed open ledger that can record transactions between two parties. | It is closed one, a single ledger that can record all the transactions between the parties. |
| It is not possible to alter single block. Because altering transaction information in one block will require alteration on the subsequent block. (all blocks are linked) | It is possible to alter a single record. All transactional records are considered separately. Also, there is no link between one record to another one. |
| blockchain are encrypted, so processing any transactions means solving complicated math problems. | The transaction did through verifying account number and balance. |
| Anyone who tries to solve these equations is rewarded with cryptocurrency in a process called “Blockchain mining”. | Only bank authorities can process the transaction. |
| If you earned any cryptocurrency, actually you could not get any physical currency, what you really get is the private key (Address) of the particular blockchain. | All your money kept safe under your account number. |
| You can use this key to withdraw money but once it lost there is no way to get your money again. | You can directly withdraw the money. If at all any problem with your account, your password will be managed by the banking system. |
| Each account has one public key, that helps others to send cryptocurrency to your account. | Your bank account number is enough to send money. |
| Blockchain chain is decentralized one, so all the transaction process is transparent to everyone in the network. | Since, the banking system is a centralized one, no one aware of others transaction detail. |
-
- It seems blockchain as an alternative to traditional banking.
-
- The bank system is a middleman concept, hence it will eliminate when everyone uses blockchain to verify their transaction.
Advantages of Blockchains
- Transparency in blockchain records makes tamper proof and secure.
- User-controlled networks, so no third-party is involved in the entire process.
- Reduced transaction costs, because no maintenance is required.
- Faster transaction settlements are achieved because blockchain works 24/7 and 365 days, unlike normal banking which relies on particular working hours.
- Decentralization of data helps to avoid the attack on the single source of data which protects from cybercriminals.
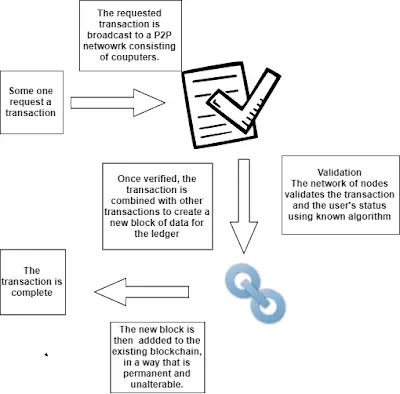 |
| Blockchain process |
Also, read:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blockchain