Research design is a detailed methodology or a roadmap for the successful completion of any research work. It is the backbone of any scientific investigation, guiding researchers through the process from hypothesis formulation to data analysis.
But why research design is so important? So, Let’s explore deeper into its significance, types, and last steps to frame a good research design. From this article, you will learn everything about research design and you can frame a good and reliable methodology for your study.
What is Research Design?
A research design is a systematic procedure that guides the process of conducting research.
It is a critical component of the research process and serves as a blueprint on how a research study should be carried out, including the methods and techniques that will be used to collect and analyze data.
A well-designed research study is important for ensuring that the research objectives are met and the results are valid and reliable.
Characteristics of a research design
Neutrality: Right from the study assumptions to setting up the study, a neutral stance must be maintained, free of preconceived concepts. A good research design should address potential sources of bias and confounding factors to be able to yield unbiased and neutral results.
Reliability: Reliability is one of the characteristics of research design that refers to consistency in measurement over repeated measures and less random errors.
Validity: Validity refers to the minimization of errors. A good research design must employ measurement tools that ensure validity of the results.
Generalizability: The outcome of the research design should be applicable to a larger population and not just a small sample. A generalized method means the study can be conducted on any part of a population with similar accuracy.
Flexibility: A research design should allow for changes to be made to the research plan as needed, based on the data collected and the outcomes of the study.
A well-structured research design is important for conducting a scientifically rigorous study that will generate neutral, reliable, valid, and reproducible results. At the same time, it should allow some level of flexibility.
Significance of Research Design
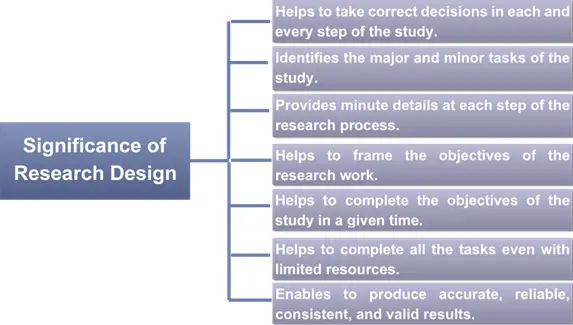
- Framing a research design helps the researcher to make correct decisions in every step of the study.
- It helps to identify the major and minor tasks of the study.
- It makes the research study effective and interesting by providing minute details at each step of the research process.
- Based on the design of experiments or research design, a researcher can easily frame the objectives of the research work.
- It helps the researcher to complete the objectives of the study in a given time and helps to complete all the tasks even with limited resources in a better way.
- A good research design enables the researcher to produce accurate, reliable, consistent, and valid results.
Elements of research design
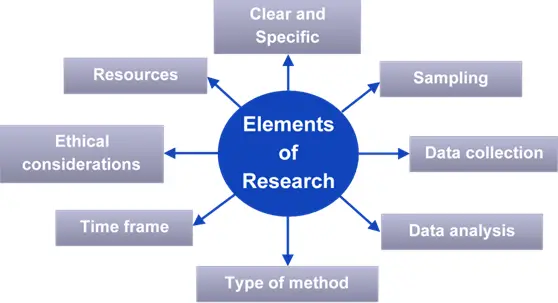
The elements of research design should be carefully planned and executed to ensure the reliability of the study findings. There are 8 major elements and which are discussed below.
Clear and Specific: The research question or hypothesis must be clearly defined and focused.
Sampling: Sampling includes decisions about sample size, sampling method, and criteria for inclusion or exclusion. It depends on the type of research design.
Data collection: This element involves the process of gathering data or information from the study participants or other sources. It includes decisions about what data to be collected, how to collect it, and what kind of tools or instruments to be used.
Data analysis: All research design types require analysis and interpretation of the data collected. This includes decisions about the statistical tests or methods that will be used to analyze the data, as well as any potential variables that need to be addressed.
Type of research methodology: It includes decisions about the overall approach of the study.
Time frame: It is an important research design element, which includes decisions about the duration of the study, the timeline for data collection and analysis, and follow-up periods.
Ethical considerations: These include decisions about informed consent, confidentiality, and participant protection.
Resources: A good research design takes into account on decisions about the budget, staffing, and other resources needed to carry out the research.
Different types of research design
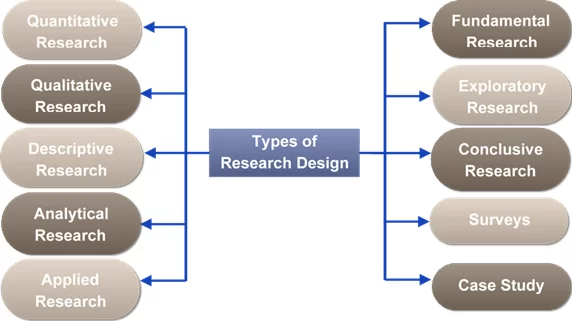
Understanding the different types of research design is essential for a researcher to draft a good research methodology which in turn helps to accomplish their research objectives in a short time. Basically, there are 10 different types. However, most researchers go for quantitative and qualitative research methods.
1. Quantitative research
Quantitative research is objective and employs statistical approaches. It establishes the cause-and-effect relationship among variables using different statistical and computational methods. This type of research is usually done using surveys, experiments, and observations which will be expressed in numbers.
2. Qualitative research
Qualitative research is subjective and experimental. It determines relationships between collected data and observations. It is usually carried out through interviews with open-ended questions, that will be described in words.
3. Descriptive or statistical research
Descriptive or statistical research outline the features of the population or issues under the study area. This type of methodology focuses more on the “what” of the research problem than the “why.” The researcher can only report the facts precisely and cannot influence the variables.
4. Analytical research
Analytical research uses proven facts to form the basis for the research. Researchers research to find supporting data that strengthens and authenticates their earlier findings. Also, it helps to develop new concepts related to the research. Thus, analytical research combines minute details to produce more acceptable hypotheses. The analytical study explains why a claim is valid.
5. Applied research
Applied research aims to solve a current issue facing by the society or an industrial organization. Applied research is considered non-systematic inquiry; a business organization, government body, or individual typically conducts this research to address a particular issue.
Fundamental research formulates theory and generalization, which are considered as the primary concerns of this research type. It seeks to discover facts with various applications, supplementing the ideas already known in a specific field or industry.
6. Exploratory research
Exploratory research is conducted for a research problem when the researcher has no past data or only a few studies available. Sometimes this research is informal and unstructured. It serves as a tool for initial research that provides a hypothetical or theoretical idea for the research problem. It will not offer concrete solutions for the research problem. It is flexible and provides the initial groundwork for future research. This research design requires the researcher to investigate different sources such as published secondary data, data from other surveys, etc.
7. Conclusive research
Conclusive research, As the name suggests it is meant to provide information that is useful in attaining conclusions or decision-making. It tends to be quantitative. In this type, the research objectives and data requirements need to be clearly defined. Findings of conclusive research usually have specific uses.
8. Surveys
Surveys help to collect a vast amount of real-time data in that way it helps the research process. It is a cost-effective method and it is usually faster than other methods. A researcher can conduct surveys in both quantitative and qualitative methods. However they usually prefer quantitative surveys as they provide numerical outputs and accurate data.
9. Case study
Case study is a common technique for qualitative analysis, which needs thorough observation of a social unit and focuses on the in-depth study. The case study emphasizes the detailed examination of a smaller set of circumstances and their interactions. This method helps to build a strong foundation for the research.
How to frame a research design?
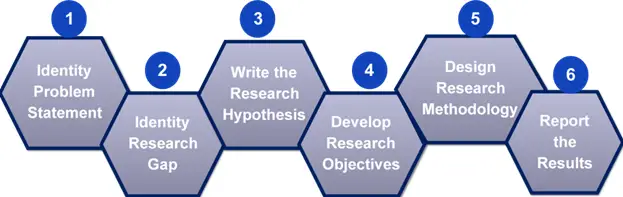
Step 1: Identify the problem statement
The very first step is, to select a novel topic of your field of research and identify the problem statement.
Step 2: Identify the research gap
- The second and most significant step is to collect pre-existing data, followed by an extensive literature survey to understand the research gap
- The step provides you a clear vision on how to proceed further with your research like the methods to be followed, data collection and analysis techniques, and tools used.
- So, you need to make a note of these important details.
Step 3: Write the research hypothesis and then write the research objectives
- The third step is to create an effective research hypothesis.
- This will assist in navigating the rest of your research process.
- Writing a research hypothesis involves numerous approaches.
- You can establish a hypothesis through the evaluation of data and analysis.
- If you are stuck for ideas, consider making a list of potential objectives and then limiting them to the most critical or relevant ones.
- Based on your hypothesis, you can develop your research objectives.
Step 4: Design research methodology
- When designing your research methodology, consider the following like type of study, sample location, sampling techniques, number of samples, experimental setup, experimental procedure, software, and tools to be used.
- By considering all these elements, you can create a good research methodology that will complete your research work.
Step 5: Analyse of data and dissemination of results
- It is time to start analyzing the data and this can be done using a different technique like descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis.
- The first step in analysis is determining which method is most suitable for analysis.
- Descriptive statistics are useful for summarising data. T-tests may be used to compare means between two groups and regression analysis can be used to investigate variable relationships.
- Once, the appropriate analysis method is chosen, analysing the data can be done.
- Then, you need to present your findings clearly with suitable interpretations.
- Finally, report your findings in the form of a research paper or thesis with appropriate discussions.
- Ensure that the research outcomes are in line with your research objectives.
Conclusion
A well-structured research design enhances the originality, reliability, and validity of your research findings. It enables the researcher to proceed in the right direction without any deviation from the tasks. Remember, a poor research design may collapse the entire research project in terms of time, manpower, and money.
Also Read: Why Research Design is Important?


