The research variable is a quantifying component that may change from time to time. In research, variables are like the building blocks that help us understand relationships between different factors. In this article, iLovePhD explains the main types of variables and what they mean with some real-world examples.
The terms variable and constant refer to changes in statistical patterns of random or real data that can lead to changes in the system’s resulting state.
In other words, variables are any characteristics that can take on different values, such as age, test marks, temperature, pressure, and weight.
Types of Research Variables with Examples
There are several types of research variables, including independent variables, dependent variables, and extraneous variables. Here’s an explanation of each type with examples:
- Independent Variables (IV)
- Dependent Variables (DV)
- Control Variables
- Extraneous Variables
- Mediating Variables
- Moderating Variables
Dependent and independent variables are measured during experimental studies to assess the cause-and-effect relationship.
1. What is a Dependent Variable in Research?
A dependent variable is a variable that varies concerning changes in the independent variable. The value of the dependent variable depends on the value of the independent variable. In statistics, dependent variables can be categorized into:
- Response variables (It varies with another variable)
- Outcome variables (It represents the outcome of another variable)
- Left-hand-side variables (It appears on the left-hand side of a regression equation)
The dependent variable is what we measure after varying the independent variable from low to high. This measurement is done to study the effect of the dependent variable on the independent variable by conducting statistical analyses. Based on the results, the degree to which the independent variable variation can be studied.
2. What is an Independent Variable?
An independent variable is a variable that we vary in an experimental study to measure its effects. It is called “independent” as it is not affected by any other variables in the study. Independent variables can be categorized into:
- Explanatory variables (It explains an event or result)
- Predictor variables (It predicts the value of a dependent variable)
- Right-hand-side variables (It appears on the right-hand side of a regression equation).
These terminologies are used in statistics, where we can study the degree to which an independent variable change can predict changes in the dependent variable.
Also Read: What is an Independent Variable? Importance and Examples
Types of independent variables
There are two main types of independent variables.
- The experimental independent variables can be directly varied during the experimental study.
- A subject variable cannot be varied, but it can be used to group research subjects categorically.
The Independent variable is the cause. Its value is independent of other variables.
ilovephd.com
The dependent variable is the effect. Its value is based on the changes in the independent variable.
Example: Independent and dependent variables
You conduct a study to assess whether changes in pressure affect the reactor performance.
Your independent variable is the pressure of the reactor. You can vary the pressure by making it low for 30 minutes and high for another 30 minutes.
Your dependent variable is the performance of the reactor. Now, calculate the performance of the reactor and analyze the change in pressure have an effect on reactor performance.
How to Find Dependent and Independent Variables in Research?
Ascertaining dependent and independent variables can be difficult or tricky while designing research experiments. A dependent variable in one research study can be the independent variable in another study; therefore, it’s important to identify the variables while formulating the design of experiments.
Tips to identify the dependent variable type:
The following research questions can be used to identify the dependent variable:
- Is this variable calculated as an outcome of the study?
- Is this variable dependent on another variable in the experimental study?
- Is this variable calculated only after other variables are changed?
Tips to identify the independent variable type:
The following research questions can be used to identify the independent variable:
- Is this variable controlled or varied as a subject grouping method?
- Does this variable come before the other variable in time?
- Is this variable used to study the effect of another variable?
Dependent and independent variables are used in the experimental and quasi-experimental research study. Some of the research questions and their dependent and independent variables are listed.
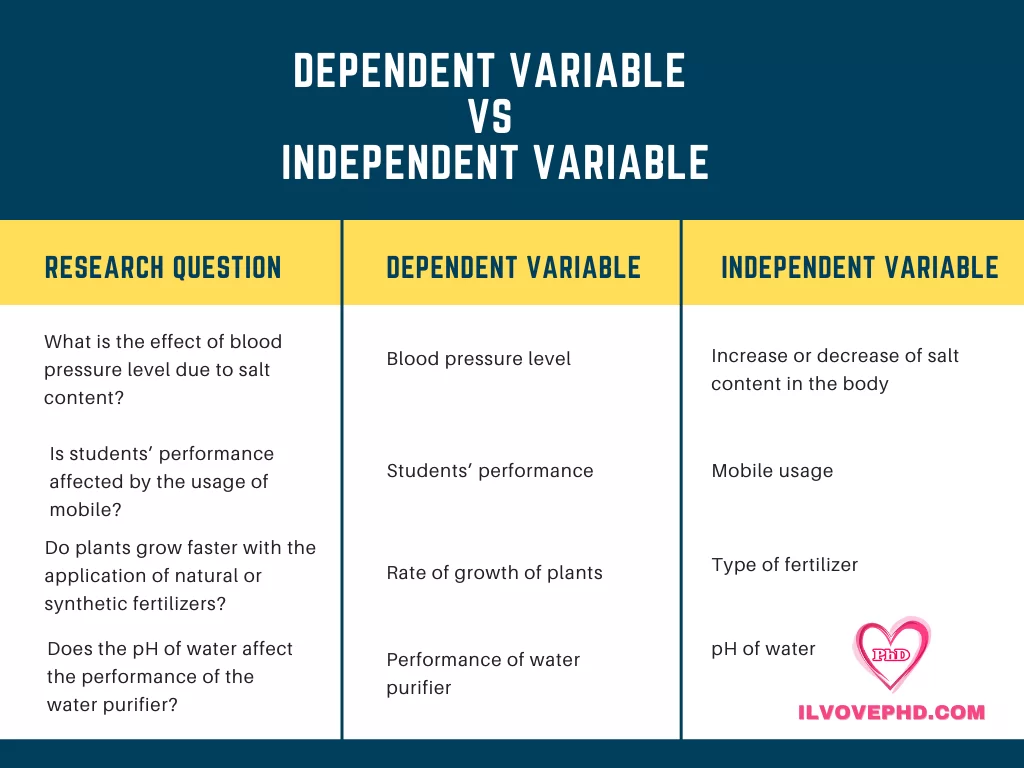
The results can be analyzed by generating descriptive statistics and an appropriate statistical test method can be used to test the research hypothesis. The type of test method depends on the type of variable, level of measurement, and number of independent variables. Most often, t-tests or ANOVA tests are used to assess the experimental data.
3. What are Control Variables?
Think of control variables as the things you want to keep constant so they don’t mess up your results. Going back to our studying methods example, let’s say you’re worried that the student’s prior knowledge might affect their scores. To control for this, you might make sure that all the students have similar levels of background knowledge before starting the study. By doing this, you’re preventing any outside factors from sneaking in and affecting your results.
- These are variables that are held constant or controlled to prevent them from confounding the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- They help ensure that any observed effects are due to the independent variable and not to other factors.
- Example: In the exercise and weight loss study, controlling for participants’ diet would be important to isolate the effects of exercise on weight loss.
4. What are Extraneous Variables?
These are like the unexpected guests at your research party – they can mess things up if you’re not careful. In our study, extraneous variables could be things like the students’ motivation levels, how much sleep they got the night before the exam, or even their access to study materials. These factors aren’t what we’re studying directly, but they could still influence the results if we’re not mindful of them.
- These are variables other than the independent and dependent variables that may influence the outcome of a study.
- They can introduce error or bias into the results if not controlled.
- Example: In the exercise and weight loss study, extraneous variables could include participants’ metabolism, genetics, or adherence to the exercise regimen.
5. What are Mediating Variables?
Sometimes, there’s a middleman in the relationship between our independent and dependent variables. Let’s say you’re studying the effect of stress on job performance. Coping mechanisms could be a mediating variable – they’re what’s happening in between the stress levels (independent variable) and how well someone does their job (dependent variable). Understanding these mediating variables helps us see the whole picture of what’s going on.
- These are variables that explain the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- They provide insight into the underlying mechanisms or processes through which the independent variable affects the dependent variable.
- Example: In a study on the relationship between stress (IV) and health outcomes (DV), coping mechanisms could serve as mediating variables, explaining how stress affects health.
6. What are Moderating Variables?
Finally, moderating variables are like the conditions or factors that can change the strength or direction of the relationship between our independent and dependent variables. For instance, in a study on the effects of exercise on mood, age could be a moderating variable. Maybe exercise has a stronger effect on mood for younger adults compared to older adults. Identifying these moderating variables helps us understand when and for whom our findings might hold.
- These are variables that influence the strength or direction of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
- They indicate under what conditions or for whom the relationship holds.
- Example: In a study on the effects of teaching methods (IV) on academic performance (DV), students’ prior knowledge could be a moderating variable, influencing how effective different teaching methods are for different students.
By understanding and considering these different types of variables, researchers can design more accurate studies and draw meaningful conclusions from their findings.
We hope that this article helps you to understand what is research variable and how to identify research variable types for designing experiments.
1. How to define variables?
A variable is any characteristic or value that can change or vary within a study. In research, variables help measure, test, and analyze relationships or differences between data points.
2. How do I choose a variable for my research?
Identify your research goal, then select variables that help answer your main research question. Ensure they are measurable, relevant, and feasible to collect data on.
3. What are examples of variables in experiments?
Examples include:
- Temperature (°C)
- Light intensity (lux)
- Number of study hours
- Test scores
These can be independent or dependent, based on the research setup.
4. What are the 4 types of variables?
- Independent – the variable you manipulate
- Dependent – the outcome you measure
- Controlled variables kept constant
- Extraneous – unwanted variables that could affect the results
5. What’s a good example of a dependent variable?
In a study measuring the effect of study time on grades:
- Dependent Variable: The exam score
It changes based on how much time was spent studying.
6. How to name variables?
Use short, descriptive names that reflect the data they represent. For example, use studyHours instead of x or var1.
7. What are variables examples?
- Age (years)
- Height (cm)
- Gender (Male/Female)
- Blood pressure (mmHg)
- Academic grade (A, B, C…)
8. What is a dependent and an independent variable in research?
- Independent Variable (IV): The cause (e.g., sleep hours)
- Dependent Variable (DV): The effect (e.g., memory score)
9. What are the 6 common types of variables in research?
- Independent
- Dependent
- Controlled
- Extraneous
- Moderating
- Mediating
10. What kind of variable is age?
Age is a quantitative, continuous variable. It can act as either an independent or dependent variable, depending on your hypothesis.
11. How do I identify variables?
- Identify what changes (Independent)
- Identify what you measure (Dependent)
- Identify what stays constant (Controlled)
12. What are examples of categorical variables?
- Gender (Male, Female)
- Blood Type (A, B, AB, O)
- Education Level (High School, Bachelor’s, Master’s)
13. What are the 3 main variables?
- Independent Variable
- Dependent Variable
- Controlled Variable
These are essential in any experiment-based research.
14. Can a study have 3 dependent variables?
Yes. Studies can analyze multiple dependent variables if they relate to the same hypothesis and are logically connected.
15. What are the 3 major types of relevant variables explained?
- Independent – manipulated to observe the effect
- Dependent – outcome observed
- Control – held constant to ensure a fair test
16. How many variables should a study have?
It depends on complexity. Typically, 1-2 independent and 1-3 dependent variables are manageable and effective.
17. What are the 10 variables?
Commonly recognized types include:
- Independent
- Dependent
- Controlled
- Extraneous
- Confounding
- Moderating
- Mediating
- Categorical
- Continuous
- Discrete
18. What are the big five variables?
This could refer to psychological traits in behavioral studies:
- Openness
- Conscientiousness
- Extraversion
- Agreeableness
- Neuroticism
However, in general research, the big five can mean common variable types: independent, dependent, controlled, extraneous, and moderating.
19. What is a variable with an example?
A variable is something measurable that can vary.
Example: In a health study, daily sugar intake is a variable.
20. What is the 5 variable statistics?
The five-number summary in statistics:
- Minimum
- First quartile (Q1)
- Median (Q2)
- Third quartile (Q3)
- Maximum
These help describe variable distribution.
21. How do you determine a variable?
Review the research aim and ask:
- What do I measure?
- What do I control?
- What do I manipulate?
22. How do you identify basic variables?
Start by reading your hypothesis:
- Cause = Independent
- Effect = Dependent
Then check other conditions you need to control.
23. What is an example of a dependent variable?
In a study on water and plant growth:
- Dependent Variable: Height of the plant
It changes with water quantity.
24. What are examples of research variables?
- Time spent on mobile phones
- Number of cups of coffee
- Blood sugar levels
- Job satisfaction ratings
25. What is an example of a case vs variable?
- Case: A single participant (e.g., Student A)
- Variable: A characteristic measured from the case (e.g., GPA)
26. What are the 7 types of variables in research?
- Independent
- Dependent
- Controlled
- Confounding
- Mediating
- Moderating
- Extraneous
27. What are the 5 major variables in research?
- Independent
- Dependent
- Controlled
- Extraneous
- Confounding
28. What are least 5 examples of variables?
- Exam score
- Daily exercise time
- Gender
- Eye color
- Income level
29. How are key variables defined in research?
Key variables are those directly involved in testing the research question. They are operationally defined, meaning they are explained in terms of how they will be measured or categorized.
30. How are variables defined in research?
They are classified based on their role (independent, dependent, etc.) and clearly defined with methods for data collection or observation. This ensures accuracy and repeatability.
Hand-Picked Related Articles
Quantitative Vs Qualitative Research
What is Hypothesis in Research? Types, Examples, & Importance